From the Editor
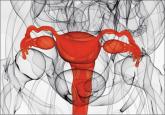
Uterus transplantation: Medical breakthrough or surgical folly?
Although uterus transplantation has been proven to be feasible, is it practical or ethical?
Q&A with Tommaso Falcone, MD

Dr. Falcone is Professor and Chair, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, at the Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio.
The author reports no financial relationships relevant to this article.

The Cleveland Clinic embarks on treating uterine factor infertility
In this Article
After previous attempts in Turkey and Saudi Arabia, the first successful uterine transplantation occurred in 2013. The team of successful surgeons was located in Gothenburg, Sweden, led by Mats Brännström, MD. The team performed 9 transplants in all, and the first birth of a healthy baby boy in October 2014 marked a medical breakthrough.1 The woman who received the transplanted uterus was born without one, a condition known as Mayer-Rokitanksy-Küster-Hauser syndrome, a cause of uterine factor infertility (UFI).
The previous options for having a child for women with UFI (which is the absence of a functional uterus, either congenital or acquired) were adoption or a gestational carrier/surrogacy.2 Surrogacy is not an option for many women, however, as in many countries, including Sweden, the use of gestational carriers and its associated contracts is illegal. All Muslim countries prohibit gestational carriers. Surrogacy also is prohibited in 3 US states, including New York, Michigan, and Arizona. Laws in other US states vary widely.3
Tommaso Falcone, MD, professor and chair, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, at the Cleveland Clinic in Cleveland, Ohio, is now co–Principal Investigator on a clinical trial assessing uterine transplantation at his institution, the first such surgeries to be performed in the United States. There will be 7 phases involved in the study: primary and secondary screening, medical evaluation, in vitro fertilization (IVF) with cryopreservation of sufficient number of embryos, transplantation and use of antirejection drugs, embryo transfer, pregnancy/delivery, and ultimately removal of the transplanted uterus. The study team is approved to enroll 10 women.4
OBG Management recently caught up with Dr. Falcone on his groundbreaking, and controversial, endeavor.
OBG Management: When did the thought of performing uterus transplantation enter your mind?
Tommaso Falcone, MD: The idea for uterus transplants was brought to my attention for the first time in Boston in 2007, at an annual meeting of the International Society for Fertility Preservation (ISFP). It was the inaugural meeting for ISFP, a society focused on helping women with cancer to protect their fertility. In 2007, we talked about the standard topics regarding fertility preservation: IVF and ovarian tissue cryopreservation. Then, right at the end of the meeting, was a presentation on uterus transplantation. Upon hearing the presenter, my thought was, “This will never happen in America, for many reasons.”
As time went on, I concentrated my energy more on ovarian tissue transplants for fertility preservation. Then a couple of years ago Andreas G. Tzakis, MD, a transplant surgeon from the University of Miami joined the Cleveland Clinic Florida. Dr. Tzakis was involved with the Swedish Group, including Mats Brännström’s transplant work in humans.
Of course, Dr. Tzakis had had a completely different journey to lead him to uterus transplantation. But as the director of solid organ transplant surgery at the Cleveland Clinic hospital in Florida, he said to me, “I think we should do this. There are many women who have asked for this procedure.” I was not sure at first, but I was interested in going to Sweden to see Dr. Brännström perform his last of 9 uterus transplants.
In Sweden, I asked Dr. Brännström if I could meet the women he already had performed the transplants on. I had certain preconceived notions on which types of women would accept this kind of major surgery to treat their infertility due to absence of a uterus. I expected perhaps that these women could have been coerced into accepting this surgery as a plausible option since surrogacy was not possible for them. I found out, as people usually do, that my preconceived notions were wrong. The women that I met said, “No, we’ve done this because we wanted to.” The women had independently come to a decision that experiencing pregnancy was important in their lives. There was no coercion. They understood the risks. However, I did not meet the uterus donors.
When I got on the plane to return home, I said to myself, we have to offer this service because it is part of the choices that women have to treat their reproductive infertility.
OBG Management: What are the hurdles you have had to overcome to bring this groundbreaking surgery to the Cleveland Clinic?
Dr. Falcone, MD: As soon as I returned from Sweden, we began the internal review board (IRB) approval process, which was extremely long. The first decision was: Do we use a live donor, as they do in Sweden, in America?
We analyzed the data from the Swedes and found that the surgery is very long for the donor and it put some of the donors, especially those who were older and placed on hormones, at risk for venous thromboembolism. (No blood clots had occurred in the Swedish trial.) In addition, there were some complications for patients. Although not major complications, we felt that these could be limited.

Although uterus transplantation has been proven to be feasible, is it practical or ethical?

Egg freezing is no longer deemed “experimental.” Here are current protocols, fertility expectations, and safety outcomes as well as ethical...
Letters from readers

Three recent recommendations, on clomiphene, immunization, and postsurgical adhesions, may affect how you practice. These experts get to the heart...
